![]() Make Appointments 24/7, 365 days a year.
Make Appointments 24/7, 365 days a year. ![]() 302-731-2888
302-731-2888
![]() Make Appointments 24/7, 365 days a year.
Make Appointments 24/7, 365 days a year. ![]() 302-731-2888
302-731-2888
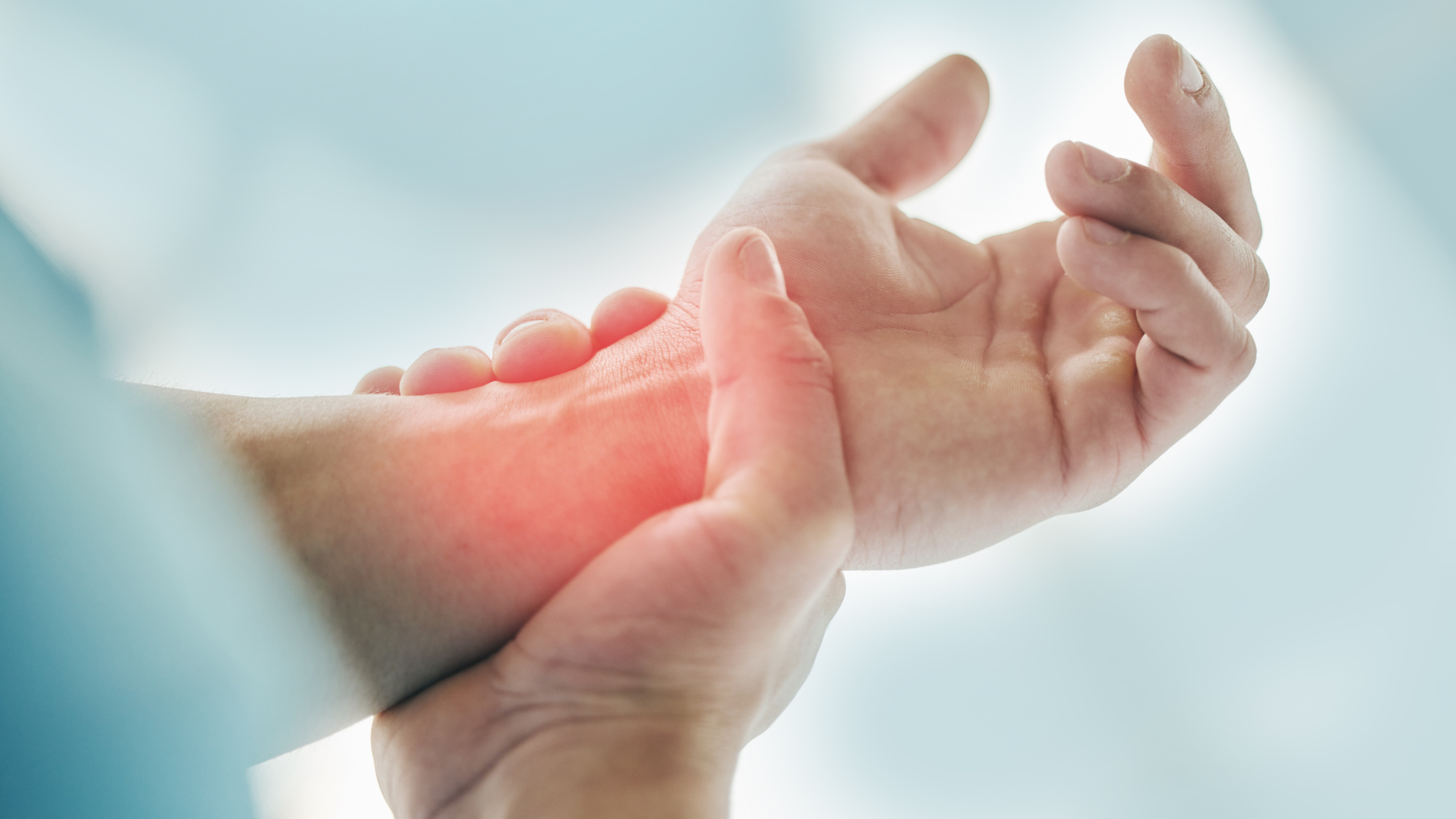
If you have been experiencing a tingling or numbness in your hands after a long day of typing, you may be suffering from carpal tunnel syndrome. Your carpal tunnel is the median nerve which runs down the palm of your hand. It provides the sensation and ability to feel to your thumb, index finger, long finger, and part of your ring finger as well as supplying the impulse to the muscle running to the thumb. When swelling occurs inside your hand and wrist which presses down or compresses your median nerve, you develop carpal tunnel syndrome, leading to numbness, tingling, and weakness on the side of your hand nearest your thumb. Carpal tunnel syndrome often develops in both hands at the same time. You will experience the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome in your hands, wrists, and possibly even your arms as the condition sets in. The most common symptoms are: Tingling or Numbness — You may feel this in your fingers or your hand. It is most commonly reported in the thumb or index finger and almost never in the little finger. The feeling may eventually begin to travel through your wrist and up your arm. The numb feeling may become constant or permanent with time. Electric Shock — You may experience a sensation which feels like an electric shock in the fingers experiencing the tingling. Weakness — Your hands may feel weak and your may drop objects as your thumb's pinching muscles grow weak as the median nerve controls them. Most cases of carpal tunnel syndrome have numerous factors lending themselves to the condition. Some of the most common causes include: Heredity — The condition seems to run in certain genetic lines within a family. Gender — Women are more likely to develop the condition than men. Age — Older individuals are more likely to suffer from the condition than younger. Repetitive hand use — If you find yourself repeating the same basic hand or wrist motions and activities over a prolonged period of time it is likely aggravating the tendons in the wrist which causes the swelling and compression of the nerve. Hand and wrist position — Activities which involve extreme flexion or extension of the hand and wrist over a prolonged period of time often increase pressure on the nerve and can lead to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. Pregnancy — Hormonal changes during pregnancy may cause swelling and lead to carpal tunnel syndrome. Health — There are many larger conditions which seem to contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome including diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid gland imbalance. Depending upon how far along your carpal tunnel syndrome has progressed, there are several treatment options to consider with your doctor. Exercise — Stretching and strengthening the muscles in your hands may help alleviate the pain you are experiencing. Lifestyle Changes — Taking breaks throughout the day from the repetitive motions you are engaging in or changing the position of your hands and wrists to a healthier one may work wonders for your condition if you are in the early days. Immobilization — Wearing a splint or brace on your hand and wrist to stop it from moving and lessening the pressure on your nerves overnight may help reduce the swelling. Medication — Anti-inflammatory drugs or certain steroid shots may help reduce the swelling. Surgery — A surgical procedure known as carpal tunnel release can increase the size of your carpal tunnel and ease pressure on your nerves if none of the other options have worked for you. If you feel that your hands have been growing weaker over time and you may be developing carpal tunnel syndrome, don't wait any longer. Contact First State Orthopaedics today to make an appointment and discuss your options to stop your carpal tunnel syndrome from progressing further.What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Symptoms
What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Treatment Options
Seek Help Today
* indicates a required field.